In today’s digital age, the collection and exchange of personal information have become integral to the functioning of numerous industries. This section delves into the complex framework that governs the activities of entities that facilitate the transfer of such sensitive information among various stakeholders. While these intermediaries play a crucial role in the modern economy, their operations are not devoid of scrutiny and regulation.
The focus here is on understanding the intricate web of rules and standards that dictate how these information handlers must conduct their business within the American legal system. From privacy protections to consumer rights, the regulatory environment is continually evolving, reflecting the dynamic nature of technology and its impact on society. This exploration aims to provide clarity on the current state of affairs and the potential future directions of this critical sector.
Moreover, this discussion highlights the importance of compliance with existing statutes and the implications of non-compliance for these intermediaries. It also touches upon the broader societal implications of their activities, including the balance between economic utility and individual privacy rights. Through this lens, we can better appreciate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for all parties involved in this multifaceted industry.
Understanding Data Brokerage
Regulatory Framework Overview plays a crucial role in governing the operations of entities that collect, analyze, and sell personal information. This section delves into the complex network of laws and regulations that dictate how these entities function within the United States.
The regulatory environment is multifaceted, involving federal statutes, state laws, and various administrative guidelines. At the federal level, key pieces of legislation such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) provide foundational rules for information handling and privacy protection. These acts set standards for transparency, consumer access, and the accuracy of personal records.
Additionally, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) serves as a watchdog, enforcing compliance with consumer protection laws and investigating deceptive practices. The FTC’s role is pivotal in ensuring that entities adhere to ethical standards and do not misuse personal information.
State laws also contribute significantly to the regulatory framework. For instance, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) introduce stringent requirements for transparency and consumer rights, including the right to access and delete personal information. These state-level regulations often set a precedent for other states and can influence federal policy.
The interplay between federal and state regulations creates a dynamic and sometimes challenging compliance environment for entities involved in the collection and sale of personal information. Understanding these regulations is essential for ensuring legal operations and safeguarding consumer privacy rights.
In summary, the regulatory framework overview highlights the intricate balance between protecting consumer privacy and allowing entities to operate within a lawful and ethical framework. It underscores the importance of ongoing compliance efforts and the need for entities to stay abreast of evolving legal requirements.
Regulatory Framework Overview
This section delves into the intricate web of rules and regulations that govern the collection, processing, and dissemination of personal information by entities involved in the trade of such information. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these frameworks protect consumer rights and ensure ethical practices within the industry.
Key Regulations and Acts: Several pivotal pieces of legislation form the backbone of the regulatory environment. These include the Federal Trade Commission Act, which empowers the FTC to oversee unfair or deceptive practices, and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, which mandates financial institutions to explain their information-sharing practices to their customers.
Role of Federal Agencies: Federal agencies play a crucial role in enforcing these regulations. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is particularly active, monitoring compliance and taking action against entities that violate consumer privacy rights. Additionally, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) focuses on ensuring that financial information is handled securely and transparently.
State-Level Initiatives: Beyond federal regulations, various states have enacted their own laws to further protect consumer privacy. For instance, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) grants residents significant rights over their personal information, including the right to know what information is collected about them and the right to have it deleted.
International Considerations: The regulatory framework also considers international standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, which sets a high bar for data protection and privacy rights. These international regulations influence how U.S. entities manage and protect information that originates from or is shared with international sources.
Challenges and Future Directions: Despite these efforts, challenges remain. The rapid evolution of technology and the increasing complexity of information networks necessitate ongoing updates to regulatory frameworks. Future directions may include more stringent requirements for transparency, stronger enforcement mechanisms, and broader consumer rights.
Consumer Privacy Rights
Safeguarding personal information is a cornerstone of modern digital society. This section delves into the rights individuals possess to protect their sensitive details from unauthorized use and exposure. It explores how consumers can exercise control over their own information in an era where personal data is constantly collected and utilized.
Consumer privacy rights encompass a broad spectrum of protections aimed at ensuring that personal information is handled responsibly and ethically. These rights are designed to empower individuals by giving them the authority to dictate how their data is used, shared, and stored. Key aspects include the right to be informed about the collection and use of personal data, the right to access one’s own information, and the right to have inaccuracies corrected.
Furthermore, consumers have the right to request that their data not be sold or shared without explicit consent. This is particularly crucial in contexts where personal information might be used for marketing or profiling purposes without the individual’s knowledge or agreement. The ability to opt-out of such practices is a fundamental aspect of maintaining privacy in the digital age.
Implementing these rights requires robust mechanisms for data protection and transparency. Companies must be held accountable for adhering to privacy standards and must provide clear, accessible information about their data practices. This includes detailing what information is collected, why it is collected, and how it will be used, as well as offering straightforward options for consumers to manage their privacy settings.
In conclusion, consumer privacy rights are essential for fostering trust in digital services and protecting individuals Remove your info from BlockShopper potential misuse of their personal information. By upholding these rights, society can ensure that the benefits of digital technology are enjoyed without compromising personal privacy and security.
Data Broker Operations
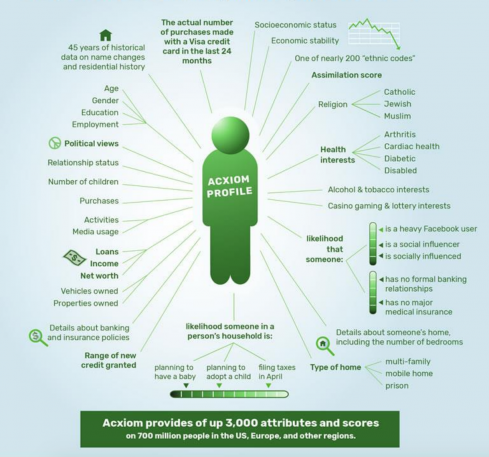
Exploring the Mechanisms of Information Aggregators: This section delves into the intricate processes through which entities collect, manage, and distribute personal details. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these operations function and their implications for individual privacy and security.
Information aggregators typically engage in extensive collection methods, ranging from public records to online activities. These entities often utilize sophisticated algorithms and data mining techniques to compile detailed profiles of individuals. The operations encompass a variety of sources, including social media, purchase histories, and even geolocation data.
Data Management and Integration: Once collected, the information is meticulously organized and integrated into comprehensive profiles. This process involves categorizing data into specific segments such as demographic, financial, or behavioral categories. The efficiency of this integration is crucial for the utility and accuracy of the profiles created.
Distribution and Utilization: The final phase of these operations involves the dissemination of compiled information to various clients, which may include marketers, researchers, or even governmental bodies. The utilization of this data can significantly influence targeted advertising, market research, and policy-making. However, it also raises critical concerns regarding consent and the ethical use of personal information.
In conclusion, the operations of information aggregators are multifaceted and impactful, influencing numerous aspects of modern life. Understanding these processes is essential for addressing the challenges they pose to privacy and security.
Compliance Challenges
Navigating the complexities of regulatory adherence is a critical aspect for entities engaged in the collection and dissemination of personal information. This section delves into the multifaceted challenges that organizations face in ensuring they meet the stringent requirements set forth by various governing bodies.
One of the primary hurdles in this domain is the diverse and often conflicting regulations across different jurisdictions. Companies must meticulously track and interpret these rules to avoid legal pitfalls. Additionally, the rapid evolution of technology and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats add layers of complexity to the compliance process.
Another significant challenge is the balancing act between operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. Implementing robust security measures and privacy protections can sometimes hinder business processes, requiring innovative solutions to maintain both security and productivity.
Furthermore, the transparency and communication with consumers about how their information is used and protected is a critical yet challenging aspect of compliance. Ensuring that this communication is clear, comprehensive, and accessible to all stakeholders is essential for maintaining trust and legitimacy.
In conclusion, while the pursuit of compliance is fraught with challenges, it is imperative for organizations to adopt a proactive and strategic approach. By investing in robust compliance frameworks and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, entities can navigate these challenges effectively and safeguard both their operations and the privacy of individuals.
Impact on Personal Security
This section delves into how the activities of information aggregators affect the safety and privacy of individuals. As these entities collect and manage vast amounts of personal details, the implications for personal security are profound and multifaceted.
The accumulation of personal information by these entities can lead to significant vulnerabilities. If not properly safeguarded, this data can be exploited by malicious actors, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and other serious crimes. Moreover, the misuse of personal information can result in social stigma and reputational damage, affecting individuals’ personal and professional lives.
Furthermore, the accessibility and dissemination of personal details can undermine individuals’ sense of security and privacy. The fear of unauthorized access to sensitive information can lead to heightened anxiety and stress, impacting mental health and overall well-being. This section will explore these issues in detail, examining the various ways in which personal security is compromised and discussing potential mitigation strategies.
Additionally, the integration of personal information into various platforms and services can create complex security challenges. As technology advances, the methods of data protection must evolve to keep pace with emerging threats. This includes the development of robust encryption techniques, stringent access controls, and comprehensive data governance policies.
In conclusion, the impact on personal security is a critical aspect that must be addressed in the context of information aggregation. By understanding the risks and implementing effective safeguards, it is possible to mitigate the adverse effects and ensure the protection of individuals’ privacy and security.
Legislation Evolution
This section delves into how the regulatory environment has transformed over time, focusing on the pivotal role of federal agencies in shaping and enforcing rules that govern the collection, use, and protection of personal information. It explores the evolution of legislative measures and the agencies responsible for their implementation.
Historically, the oversight of information handling practices was fragmented, with various agencies addressing different aspects of the issue. However, recent years have seen a more coordinated approach, driven by the recognition of the interconnectedness of privacy and security concerns.
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC): The FTC has been at the forefront of regulating information collectors, emphasizing consumer protection and fair business practices. It has taken numerous actions against entities that mishandle personal information, setting precedents that influence future legislation.
- Department of Commerce: This department has played a significant role in promoting the adoption of best practices and standards for information security. It has also facilitated dialogues between the private sector and government to enhance the resilience of the digital infrastructure.
- National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA): The NTIA has been instrumental in advocating for comprehensive privacy policies, particularly in the digital realm. It has worked closely with stakeholders to draft guidelines that balance innovation with user privacy.
- Office of Management and Budget (OMB): The OMB has overseen the implementation of federal privacy policies, ensuring alignment with broader governmental objectives. It reviews and approves privacy impact assessments, thereby influencing how agencies manage sensitive information.
The collaboration among these agencies has been crucial in developing a coherent regulatory framework. Their efforts have not only addressed current challenges but also prepared the ground for future regulatory advancements, ensuring that the governance of personal information remains robust and responsive to technological changes.
Looking ahead, the role of federal agencies is likely to expand as new technologies emerge and the digital landscape continues to evolve. Their continued engagement and innovation in policy-making will be essential to protect individual rights and maintain public trust in the digital economy.
Role of Federal Agencies
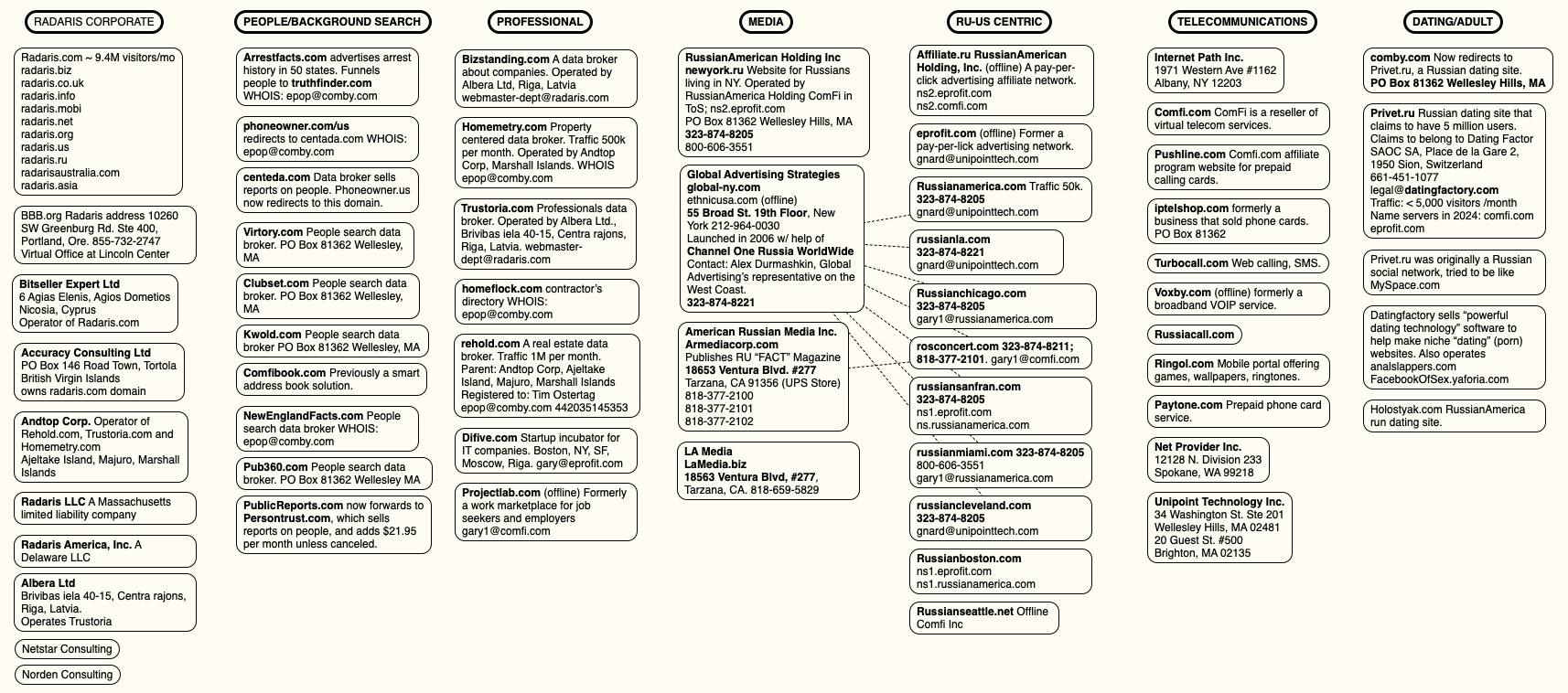
This section delves into how various federal agencies contribute to the oversight and regulation of information intermediaries in the United States. These agencies play a crucial role in ensuring that practices within the industry align with consumer protection laws and national security interests.
Federal agencies are instrumental in shaping the regulatory environment for information intermediaries. They enforce laws, provide guidelines, and sometimes collaborate to address complex issues that arise from the collection, processing, and dissemination of personal information.
| Agency | Role | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Trade Commission (FTC) | Primary regulator | Enforces privacy laws, investigates deceptive practices, and provides consumer education. |
| Department of Homeland Security (DHS) | Security oversight | Monitors threats to national security, collaborates on cybersecurity initiatives. |
| Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) | Financial regulation | Ensures transparency and compliance in financial disclosures related to information handling. |
| Office of Management and Budget (OMB) | Policy coordination | Coordinates federal privacy policies and oversees compliance across government agencies. |
Each agency brings its expertise and mandate to the table, creating a comprehensive regulatory framework that addresses both the economic and security aspects of information handling. Their collaborative efforts are essential in navigating the evolving challenges posed by information intermediaries.
State-Level Initiatives

This section delves into the proactive measures undertaken by individual states to enhance privacy protections and regulate the collection and use of personal information. While federal laws provide a foundational framework, state-level efforts often address more specific concerns and adapt to local needs.
Innovative Approaches
Several states have introduced legislation aimed at strengthening consumer rights and imposing stricter controls on the acquisition and dissemination of personal data. These initiatives range from comprehensive privacy laws to targeted regulations that address specific vulnerabilities in the information market.
California’s Leadership
California, for instance, has been at the forefront with the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which grants residents extensive rights over their personal information, including the right to know what information is collected and the right to have it deleted. This law has set a precedent and influenced other states to consider similar protections.
Other State Efforts
States like Virginia and Colorado have also passed comprehensive privacy laws, each with its unique provisions. These laws not only enhance privacy rights but also impose significant obligations on entities handling personal information, fostering a more secure environment for consumers.
Challenges and Opportunities
The proliferation of state-level regulations presents both challenges and opportunities. While it creates a patchwork of rules that businesses must navigate, it also encourages innovation in privacy protection and ensures that diverse consumer needs are addressed. Coordinated efforts among states and with federal agencies are crucial to maintaining consistency and effectiveness in these regulations.
Looking Ahead
As technology evolves and the digital landscape becomes more complex, state-level initiatives will continue to play a critical role in shaping the future of privacy and information security. These efforts are essential for keeping pace with technological advancements and ensuring that the rights and interests of consumers are safeguarded.
Future Trends in Regulation
This section delves into emerging patterns in the oversight of information intermediaries. As technology advances and consumer awareness grows, regulatory bodies are expected to adapt their strategies to ensure privacy and security are maintained. The focus will likely shift towards more proactive measures and international cooperation to address the complexities of global information networks.
| Trend | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Use of AI in Compliance | Regulators may leverage artificial intelligence to monitor and enforce compliance more effectively. | Enhanced accuracy and efficiency in identifying and addressing non-compliant practices. |
| Greater Emphasis on Consumer Control | New regulations could empower consumers to have more control over their personal information. | Strengthened consumer rights and potentially reduced misuse of personal data. |
| International Regulatory Harmonization | There may be a push towards creating unified international standards for information handling. | Streamlined compliance for global companies and consistent protection for consumers worldwide. |
| Enhanced Penalties for Non-Compliance | Penalties for failing to adhere to regulations could become more severe. | Increased deterrence against non-compliance and a cleaner industry environment. |
As these trends unfold, it is crucial for stakeholders to stay informed and adaptable. The regulatory environment is poised to become more stringent and sophisticated, reflecting the evolving nature of information technology and the increasing importance of safeguarding personal privacy.
International Comparison
This section delves into how regulatory approaches vary across different countries, highlighting the diverse strategies employed to manage information intermediaries and protect consumer privacy. By examining these international frameworks, we can gain insights into potential future trends in regulation.
In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets a stringent standard for privacy rights and data protection. It mandates comprehensive consent requirements and imposes hefty fines for non-compliance, significantly influencing how information is handled across member states.
- GDPR Implementation: European nations have adopted the GDPR uniformly, ensuring a high level of privacy protection across the continent. This regulation emphasizes the rights of individuals to control their personal information.
- UK Post-Brexit: Following its exit from the EU, the UK has maintained GDPR-like regulations, indicating a continued commitment to robust privacy standards.
In contrast, the United States employs a sectoral approach, with different rules for different industries. This fragmented system can lead to varying levels of protection depending on the sector in question.
- Sectoral Regulations: Each industry, such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications, has its own set of privacy regulations, often resulting in a patchwork of protections.
- State-Level Initiatives: Some states have enacted their own privacy laws, like California’s Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which provides broader protections than federal regulations.
Asia-Pacific countries also exhibit diverse regulatory approaches. For instance, Australia and Japan have implemented comprehensive privacy laws that align with international standards, while other countries are still developing their regulatory frameworks.
- Australia’s Privacy Act: This act provides a robust framework for the protection of personal information, with regular updates to keep pace with technological advancements.
- Japan’s Act on Protection of Personal Information: This law emphasizes the importance of consent and transparency in information handling practices.
By comparing these international approaches, it becomes clear that while there is a global trend towards strengthening privacy protections, the methods and enforcement vary significantly. Understanding these differences can help inform future regulatory developments and foster a more harmonized global approach to privacy and security.
