
In the vast expanse of the digital realm, safeguarding one’s personal information has become a paramount concern. This section delves into the critical aspects of maintaining confidentiality in cyberspace, exploring how each individual’s data integrity can be protected amidst the constant exchange of information.
The Importance of Data Protection cannot be overstated in today’s interconnected world. As we navigate through various online platforms, the collection and use of our personal details are inevitable. Understanding the mechanisms by which our information is handled is crucial for maintaining control over our digital identities.
Why Guarding Your Information is Essential goes beyond mere data security; it involves the preservation of personal freedom and autonomy. The implications of not adequately protecting your digital footprint can range from minor inconveniences to severe breaches of personal security. This article aims to shed light on the strategies and tools available to enhance your cybersecurity, ensuring that your interactions online remain secure and private.
The Evolution of Digital Privacy Concerns

Over the past few decades, the realm of personal data protection has undergone significant transformations. This section delves into the historical progression of concerns related to safeguarding individual information in the digital age. It explores how societal and technological advancements have shaped the landscape of data security, highlighting key milestones that have influenced modern perspectives on this critical issue.
Early Beginnings: Initially, digital privacy concerns were minimal due to the limited scope of internet usage. However, as technology evolved and the internet became more pervasive, the potential for data misuse became apparent. The introduction of the first data protection laws marked a significant shift in recognizing the importance of digital privacy.
Rapid Technological Advancements: The proliferation of smartphones, social media, and cloud computing services in the early 21st century significantly expanded the avenues through which personal information could be collected and exploited. This era saw a surge in public awareness and concern regarding the protection of personal data, leading to more stringent regulations and the development of privacy-enhancing technologies.
Globalization and Data Flow: The global nature of the internet has complicated the enforcement of privacy laws. Different regions have adopted varying standards, leading to a patchwork of regulations that often conflict. This has necessitated international cooperation and the harmonization of privacy standards to effectively protect user data across borders.
Emerging Threats and Future Challenges: With the advent of artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and the Internet of Things, new challenges have emerged. These technologies can process vast amounts of personal data, raising ethical and legal questions about consent, data ownership, and the potential for surveillance. The future of digital privacy will likely involve adapting existing frameworks to these evolving technologies and ensuring that privacy protections remain robust in the face of these new threats.
In conclusion, the evolution of digital privacy concerns reflects a dynamic interplay between technological innovation and societal values. As we continue to navigate this landscape, it is crucial to remain vigilant and proactive in safeguarding personal information against the ever-changing backdrop of digital technology.
The Evolution of Digital Privacy Concerns
In this section, we delve into the historical progression of concerns surrounding personal data protection in the digital realm. As technology has advanced, so too have the methods and motivations behind data collection, leading to a heightened awareness and demand for safeguarding individual information.
Early Stages of Digital Privacy Awareness
Initially, the internet was viewed as a vast, open space where anonymity was the norm. However, as businesses and governments began to recognize the value of user data, concerns about how this information was being utilized started to emerge. The early 2000s saw a rise in awareness about data tracking and the implications of sharing personal information online.
The Rise of Data-Driven Businesses
With the advent of social media and e-commerce, the collection and analysis of user data became integral to business strategies. This shift not only highlighted the economic value of personal information but also raised ethical questions about consent and the extent of data usage. The public began to demand more transparency and control over their personal data.
Legislative Responses
In response to growing public concern, various legislative measures were introduced to protect digital privacy. Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States were enacted to give users more control over their personal data and to hold companies accountable for its misuse.
Technological Solutions
Simultaneously, technological advancements have been made to enhance privacy protection. Tools such as encrypted communication apps, virtual private networks (VPNs), and privacy-focused browsers have become popular as individuals seek to protect their information from unauthorized access.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the evolution of digital privacy concerns is likely to continue as new technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) become more prevalent. It is crucial for both users and policymakers to stay informed and proactive in addressing these evolving challenges to ensure a balanced approach to data use and privacy protection.
Key Components of Online Privacy

This section delves into the intricate mechanisms by which personal information is gathered and utilized across the digital landscape. It is crucial to comprehend these processes to effectively safeguard one’s digital footprint.
Data Collection Methods
In the realm of digital interactions, data collection is ubiquitous. It occurs through various means, including but not limited to, cookies, web beacons, and tracking pixels. These tools monitor user activity, capturing details such as browsing habits, search queries, and even location data. The gathered information is then often used to tailor advertisements, enhance user experience, or for more nefarious purposes if not properly secured.
Data Usage
The utilization of collected data varies widely. On one end of the spectrum, it serves to personalize content and improve services. However, it can also be sold to third parties or exploited for targeted advertising without explicit consent. Understanding the extent and purpose of data usage is fundamental to maintaining control over one’s personal information.
Consent and Transparency
A critical component of data protection is the principle of consent. Users should be fully aware of what data is being collected and for what purposes. Transparency in privacy policies and clear communication about data handling practices are essential in upholding this principle. Unfortunately, the complexity and legalese of many privacy policies often obscure this transparency, making it difficult for users to make informed decisions.
Security Measures
Protecting collected data from unauthorized access or breaches is another pivotal aspect of data privacy. Encryption, secure data storage, and regular security audits are among the practices that companies should implement to safeguard user information. The consequences of inadequate security can be severe, ranging from identity theft to financial loss.
In summary, the components of data privacy encompass the methods of collection, the purposes of usage, the principles of consent and transparency, and the security measures in place. Each element plays a crucial role in the broader context of preserving digital privacy.
How Data is Collected and Used Online
In this section, we delve into the mechanisms by which information is gathered and utilized across the digital landscape. The focus is on understanding the processes and technologies that enable the collection of user data, which is pivotal in shaping the online experience and the broader digital ecosystem.
Data collection online is multifaceted, involving various tools and methods. One of the most common tools used in this process is cookies. Cookies are small text files that websites send to a user’s device, which then store information about the user’s interactions with the site. This data can include details about the pages visited, the time spent on each page, and even the items placed in a shopping cart. The primary purpose of cookies is to enhance user experience by remembering user preferences and actions, thereby making subsequent visits more efficient.
However, cookies also play a crucial role in tracking user behavior across the web. This tracking is often used by advertisers to deliver targeted ads that are more likely to resonate with the user based on their browsing history. While this can be beneficial for users by providing relevant content, it also raises significant concerns regarding the privacy and security of personal information.
The use of cookies is regulated by various laws and guidelines aimed at protecting user data. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe mandates that users must be informed about the use of cookies and have the option to consent or refuse their use. This regulatory framework underscores the importance of transparency and user control in the collection and use of data online.
In conclusion, while cookies are instrumental in enhancing the functionality and personalization of web experiences, they also highlight the intricate balance between convenience and privacy in the digital age. Understanding how these tools operate and the implications they carry is essential for maintaining control over one’s digital footprint.
The Role of Cookies in Web Browsing
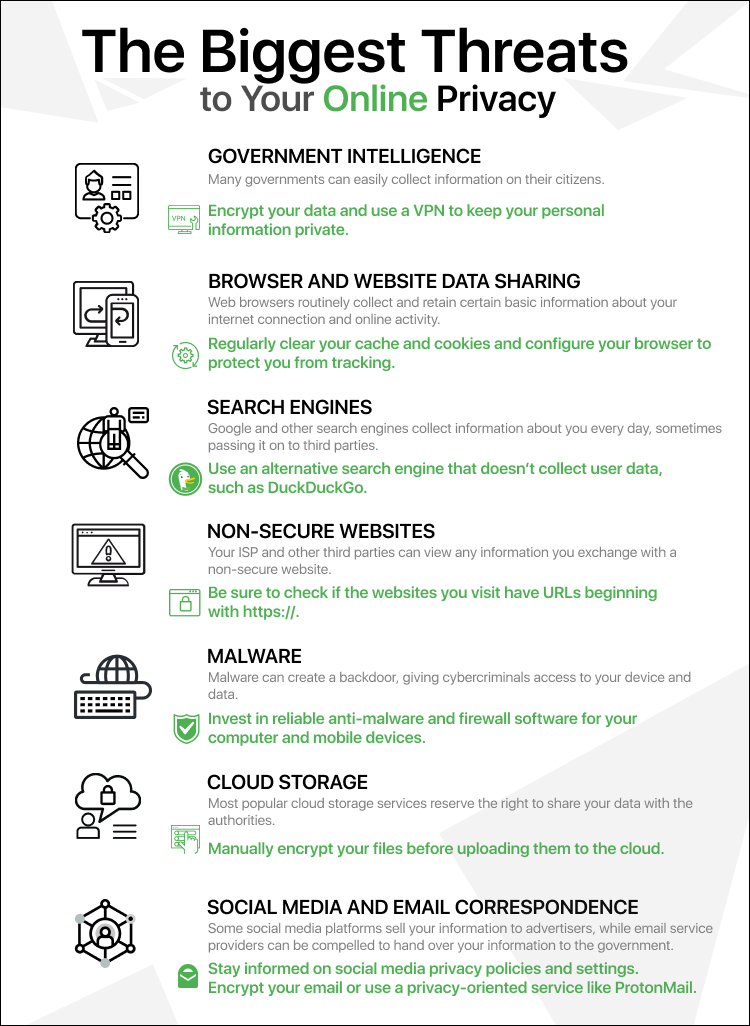
This section delves into the integral part that small text files, commonly known as cookies, play in the realm of web navigation. While enhancing user experience, these files also raise significant concerns regarding personal data management and user autonomy.
Cookies Defined
Cookies are tiny files that websites send to a user’s device, which are then stored and sent back to the same site upon subsequent visits. They serve various purposes, from remembering user preferences to tracking browsing habits, thereby playing a crucial role in the customization and functionality of web services.
Types of Cookies
There are several types of cookies, each with a distinct function. Session cookies are temporary and are erased when the user closes the browser. Persistent cookies, on the other hand, remain on the user’s device for a specified period. Additionally, first-party cookies are set by the website being visited, while third-party cookies originate from other domains and are often used for advertising and tracking across different sites.
Impact on User Experience
Cookies significantly enhance user experience by allowing websites to remember user information and settings. This can include anything from language preferences to login details, making the browsing experience more seamless and personalized.
Privacy Concerns
Despite their benefits, cookies also pose privacy concerns. They can track a user’s online activities, potentially leading to the collection of sensitive information without explicit consent. This has led to increased scrutiny and regulation, with many jurisdictions requiring websites to inform users about cookie usage and obtain their consent.
Managing Cookies
Users have the ability to manage cookies through their browser settings, including blocking or deleting them. However, doing so might limit the functionality of some websites and affect the browsing experience. It is crucial for users to understand these trade-offs and make informed decisions about their cookie settings.
In conclusion, while cookies are fundamental to the modern web experience, their role must be balanced with the need for user privacy and control over personal data. As technology evolves, so too must the strategies for managing and protecting this data.
Privacy Policies: Decoding the Fine Print
This section delves into the intricate world of privacy policies, which are often complex and overlooked by users. Despite their dense legal language, these documents play a crucial role in safeguarding personal information. Here, we aim to simplify and highlight the importance of understanding these policies to protect one’s digital footprint.
Privacy policies are legal documents that outline how an organization or website collects, uses, maintains, and discloses information from its users. They are essential for ensuring transparency and compliance with various data protection laws. However, their verbose and legalistic nature often makes them inaccessible to the average user.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Information Collection | Describes what type of information is collected (e.g., personal data, usage data). |
| Use of Information | Explains how the collected data is utilized (e.g., for improving services, marketing purposes). |
| Data Sharing | Outlines circumstances under which the data might be shared with third parties. |
| User Rights | Details the rights of users regarding their data (e.g., right to access, correct, or delete their information). |
| Security Measures | Describes the steps taken to protect user data from unauthorized access or disclosure. |
Understanding these components can empower users to make informed decisions about the services they use and the data they share. It is crucial for individuals to be proactive in reading and comprehending these policies to maintain control over their personal information in the digital age.
In conclusion, while privacy policies may seem daunting, they are a critical tool for protecting personal data. By taking the time to understand these documents, users can better navigate the complexities of digital privacy and ensure their rights are respected.
The Impact of Social Media on Personal Privacy
In this section, we delve into the profound influence that social networking platforms have on the safeguarding of personal information. The pervasive nature of these platforms necessitates a thorough examination of how they affect the protection of our private lives.
Social Media’s Role in Privacy Erosion
Social media platforms, by their very design, encourage users to share vast amounts of personal data. This sharing, while intended for connection and community building, often inadvertently exposes sensitive information to a broader audience than initially anticipated. The ease with which data can be disseminated and the lack of control over its subsequent use can lead to significant privacy concerns.
The Unintended Consequences of Sharing
Often, users are unaware of the full extent to which their shared information can be accessed and utilized. This lack of awareness can lead to situations where personal data is used in ways that are detrimental to the user, such as in targeted advertising or even identity theft.
Regulatory Frameworks and Their Limitations
Various legal frameworks have been established to protect user data on social media. However, the global nature of these platforms often means that these regulations are inconsistently applied or enforced. This disparity can leave users vulnerable, especially when their data is processed in jurisdictions with less stringent privacy laws.
The Need for Enhanced User Control
To mitigate these risks, there is a growing call for social media platforms to provide more robust tools for users to manage their privacy settings. This includes clearer explanations of how data is used and more granular controls over what information is shared and with whom.
In conclusion, while social media continues to play a pivotal role in modern communication, it is crucial that the impact of these platforms on personal privacy is continually assessed and addressed. Through enhanced user education and more stringent regulatory oversight, it is possible to foster a more secure environment for personal data sharing.
Legal Frameworks Protecting Digital Secrecy
This section delves into the intricate web of legal structures designed to safeguard individual confidentiality in the digital realm. It explores how various statutes and regulations aim to protect users from unwarranted intrusions into their personal information.
Legislation and Regulations
Numerous countries have enacted specific laws to address the protection of digital confidentiality. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union is a robust framework that imposes strict rules on data collection, processing, and transfer. It empowers users with rights such as access, rectification, and erasure of their personal data.
International Standards
Beyond national laws, international standards like the OECD Guidelines on the Protection of Privacy and Transborder Flows of Personal Data provide a global benchmark for digital confidentiality. These guidelines help harmonize approaches to data protection across borders, ensuring that individuals’ rights are respected regardless of where their data is processed.
Enforcement and Compliance
Effective enforcement of these legal frameworks is crucial. Regulatory bodies, such as the Information Commissioner’s Office in the UK, play a pivotal role in monitoring compliance and imposing penalties on entities that violate data protection laws. This enforcement not only punishes non-compliance but also serves as a deterrent against future breaches.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite these frameworks, challenges remain. The rapid evolution of technology often outpaces the ability of laws to keep up, leading to gaps in protection. Moreover, the global nature of the internet complicates jurisdiction and enforcement. Future legal developments will need to address these challenges, possibly through more collaborative international efforts and adaptive legal mechanisms.
In conclusion, while legal frameworks offer significant protection for digital confidentiality, ongoing vigilance and adaptation are necessary to keep pace with technological advancements and evolving threats to personal information security.
Tools and Techniques for Enhancing Privacy Online
In this section, we delve into the various methods and resources available to bolster personal security on the web. With the increasing complexity of digital environments, it is crucial to explore practical ways to safeguard one’s information from potential threats and unauthorized access.
One of the primary tools for enhancing digital security is the use of virtual private networks (VPNs). VPNs create a secure tunnel between your device and the internet, encrypting your data and hiding your IP address. This not only protects your information from being intercepted but also helps in bypassing geographical restrictions on content.
Another essential technique is the adoption of robust password management. Using complex, unique passwords for different accounts and employing password managers can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. These tools not only generate strong passwords but also store them securely, eliminating the need to remember multiple complex codes.
Moreover, browser extensions and add-ons that block trackers and ads can enhance your browsing experience by preventing websites from collecting your data. These tools can stop cookies and other tracking mechanisms, thereby reducing the amount of information that third parties can gather about your online activities.
Regular software updates are also crucial in maintaining digital security. Updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities, making it harder for hackers to exploit system weaknesses. Ensuring that your operating system, applications, and security software are up-to-date is a simple yet effective way to protect your digital presence.
Lastly, awareness and education about digital security practices are invaluable. Understanding the types of threats that exist and knowing how to recognize phishing attempts or suspicious emails can empower users to take proactive steps in protecting their personal information.
By integrating these tools and techniques into your daily digital routine, you can significantly enhance your online security and protect your personal information from potential breaches.
The Consequences of Privacy Breaches

This section delves into the repercussions of unauthorized access to personal information. The impact of such incidents can be far-reaching, affecting both individuals and organizations. We will explore the various ways in which these breaches can disrupt lives and undermine trust in digital platforms.
Privacy violations can lead to a range of negative outcomes. For individuals, this might include identity theft, financial loss, and emotional distress. Organizations, on the other hand, may face legal penalties, loss of customer trust, and damage to their reputation. Understanding these consequences is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent and mitigate such incidents.
| Type of Breach | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Identity Theft | Unauthorized use of personal information for fraudulent activities, leading to financial loss and legal issues. |
| Financial Loss | Direct theft of funds or unauthorized transactions resulting from compromised financial information. |
| Emotional Distress | Stress, anxiety, and fear associated with the loss of control over personal data. |
| Legal Penalties | Fines and legal actions against organizations that fail to protect user data. |
| Reputation Damage | Loss of public trust and brand value due to mishandling of sensitive information. |
In conclusion, the ramifications of privacy breaches are multifaceted and significant. They underscore the importance of robust security measures and the need for continuous vigilance in the digital age. By understanding these consequences, we can better appreciate the importance of safeguarding personal information and the role that both individuals and organizations play in this endeavor.
Global Perspectives on Internet Privacy
This section delves into the multifaceted consequences of breaches in digital confidentiality. It explores how such incidents can affect individuals and organizations on a global scale, highlighting the diverse impacts and responses from different regions.
Breaches in digital confidentiality can lead to several immediate and long-term effects:
- Financial Losses: Victims may suffer direct financial losses due to theft of banking or credit card information.
- Identity Theft: Personal data leaks can result in identity theft, causing significant damage to an individual’s reputation and financial stability.
- Legal Implications: Organizations may face legal consequences, including fines and penalties for failing to protect user data.
- Reputational Damage: Both individuals and corporations can suffer from reputational damage, which can impact business relationships and personal lives.
- Psychological Impact: The stress and anxiety associated with data breaches can have lasting psychological effects on victims.
Different regions have varying approaches to handling and mitigating the consequences of such breaches:
- Europe: With the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Europe has stringent laws that impose heavy fines on organizations that fail to protect personal data.
- Asia: Countries like China and India are developing their own frameworks, often influenced by global standards but tailored to local needs.
- North America: The United States and Canada have sector-specific regulations, leading to a patchwork of protections across different industries.
- Africa: Many African nations are still in the early stages of developing comprehensive data protection laws, often looking to international models for guidance.
Understanding these global perspectives is crucial for developing effective strategies to protect digital confidentiality and respond to breaches. It also highlights the need for international cooperation to address these challenges effectively.
Future Trends in Online Privacy Protection
As we navigate through the digital age, the safeguarding of personal information becomes increasingly crucial. This section delves into the emerging strategies and technologies that are shaping the future of data protection. The focus is on how these advancements aim to fortify the security of sensitive data against evolving threats.
One of the key trends in this domain is the development of advanced encryption methods. These techniques are designed to make data unreadable to unauthorized parties, even if intercepted. Quantum encryption, for instance, leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to secure communications, promising a leap forward in impenetrability.
Another significant trend is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) in monitoring and predicting privacy breaches. AI algorithms can analyze patterns and anomalies in data usage, providing real-time alerts and interventions to prevent unauthorized access. This proactive approach is expected to enhance the responsiveness of privacy protection measures.
Moreover, the integration of blockchain technology into privacy solutions is gaining traction. Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable ledger system can ensure that data transactions are transparent and tamper-proof, offering a robust layer of security against data manipulation and theft.
Regulatory frameworks are also evolving to keep pace with technological advancements. Countries around the world are updating their laws to better protect digital privacy, often requiring businesses to implement stricter data protection standards. This legal evolution is pushing companies to innovate in their privacy practices, driving the development of more secure systems.
In conclusion, the future of privacy protection is being shaped by a combination of technological innovation and regulatory adaptation. These trends collectively aim to create a more secure digital environment, where personal data is protected against the sophisticated threats of the modern world.
